end tidal co2 meaning
Most medical sources define hypocapnia as less than 35 mm Hg for partial CO2 pressure in the arterial blood. This causes CO2 to accumulate in the lungs and more of it to be excreted with each breath hypercapnea which would cause the ETCO2 level to rise.
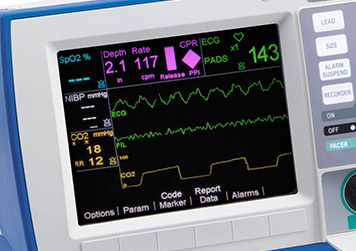
R Series End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Zoll Medical
ETCO2 is the amount of carbon dioxide CO2 in exhaled air which.

. ETCO2 is the amount of carbon dioxide CO2 in exhaled. Of or relating to the last portion of expired tidal air End-tidal carbon dioxide monitors are already being used and are recommended to indicate the adequacy of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and the likelihood of a successful resuscitation. Loss of the ETCO2 trace.
Like pulse oximetry before it alerting us to changes in oxygenation end-tidal CO2 monitoring or ETCO2 is rapidly becoming an additional vital sign. What is a normal end tidal CO2 level. So a high ETCO2 is a good sign of good ventilation while low ETCO2 is bad sign that represents hypoventilation.
The arterial CO2 value for normal breathing at. We routinely use ETCO2 to provide information on ventilation. However any number of conditions can cause a change that may or may not be considered normal for any given patient.
In the awake adult normal cardiac index lies between 25-4 Lminm2 with an ETCO2 of 35-45 mmHg. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. Mengert The New England Journal.
If a person has a very shallow breathing pattern with the tidal volume as his dead. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. It is the measurement of CO2 at the completion of exhalation and roughly correlates to the CO2 present in arterial blood.
Obviously the alveolar and arterial CO2 values increase during breath-holding. When CO2 diffuses out of the lungs into the exhaled air a device called a. For example a patient in DKA may have a very low EtCO2.
Eisenberg and Terry J. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring ETCO2 has clinical uses far beyond solely determining hypo- or hyperventilation. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG.
Edit on Wikidata Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide CO. The normal values are 5-6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. Monitoring capnography waveforms and end-tidal CO2 biofeedback during breathing exercises.
It is usually presented as a graph of CO. What does a high end-tidal CO2 mean. Its main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anesthesia and intensive care.
On average during CPR if adequate chest compressions are being delivered a cardiac index of 16-19 Lminm2 can be generated which correlates with ETCO2 pressures of 20mmHg. The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle. ETCO2 is the amount of carbon dioxide CO2 in exhaled air which assesses ventilation.
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 is the level of carbon dioxide that is released at the end of an exhaled breath. Definition of Low CO2 hypocapnia Hypocapnia hypocapnea also known as hypocarbia is defined as a deficiency of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood. End-tidal CO2 monitoring is a non-invasive way to monitor a patients carbon dioxide levels.
Similarly what does low etco2 mean. Available evidence has established that ETCO2 measurement can provide an indication of cardiac output and pulmonary blood flow24 Non. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor.
Medical Definition of end-tidal. What causes an increase in ETCO2. End tidal CO2 ETCO2 MeSH.
The gradient is the difference between the arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure PaCO 2 and the etCO 2 partial pressure is a result of the relationship between ventilation and perfusion or rather ventilation-perfusion matching VQ. This non-invasive monitor can give valuable information about cardiac output perfusion and ventilation. The height of the capnography waveform accompanies this number on the monitor as well as the.
2 in the respiratory gases. The continued presence of CO2 in the exhaled breath can only mean placement of the tube in the trachea. But CO2 levels are normal or low it may mean that the patient has a cardiac-related problem such as congestive heart.
If a person holds his breath the etCO 2 reading is going to show zero no CO2 exhaled. Yes the generic normal is considered 35-45. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG.
In severe cases of respiratory distress increased effort to breathe does. This causes CO2 to accumulate in the lungs and more of it to be excreted with each breath hypercapnea which would cause the ETCO2 level to rise. ETCO2 levels reflect the adequacy with which carbon dioxide CO2 is carried in the blood back to the lungs and exhaled.
1 ACLS guidelines define high quality chest compressions as. Secondly what does low etco2 mean. When calculating the gradient the clinician is comparing the carbon dioxide CO 2 sampled from the ABG.
This is a major respiratory symptom. Well the EtCO2 value is simply a number. End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath.
Normal end tidal co2 values. Both end-tidal CO2 monitors and pulse oximetry devices work closely together to help monitor the respiratory status of a patient.

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training
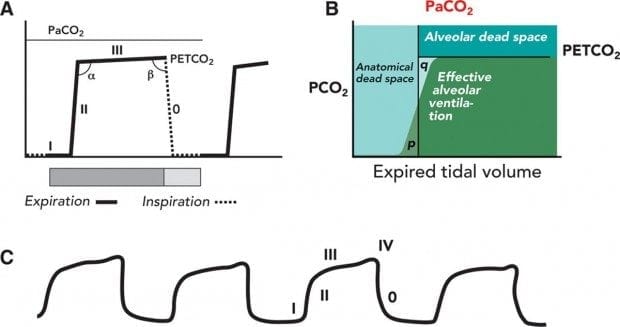
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog
End Tidal Co2 The Drummer Of The Vital Sign Band Pem4
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice
The Normal Capnograph Waveform Deranged Physiology

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog

Normal And Abnormal Capnography Waveforms Infographic Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Basic Waveform Capnography As A Continuous Monitoring Tool During Mechanical Ventilation

